能源监控解决方案Load management
Load management
|
Coupling X-Meter or X-RWU Gold to XM18 function and the optional hardware XM15, it’s possible to carry out complex logics for releasing the loads in order to avoid excess of contracted power with the energy supplier. This is possible by means of a refined algorithm which progressively drives opening and closing of a set of loads, after programmed a series of priorities which can be managed. Technically, X-Meter or X-RWU Gold must measure the general power on the delivery point. This can be made in two ways:
|
|
The thresholds and priorities setting allows you to activate one of the four instrument’s outputs which drives XM15 module. This module contains 4 relay with two exchange-switches which act to cut off and reinsert the 4 connected loads.
If the loads are more than 4, it’s possible using further instruments connected among them. All these instruments, such as the first one, measure the power on the delivery point and front time to time they are enabled for cutting off further loads, when the interruption of the previous loads hasn’t been enough to avoid the overcoming of power. You can select the integration time from 1 to 60 minutes (default is 15’) and the management of the loads will be carried out always according to the average value calculated on the selected time of integration. The average value may be steady or floating, it depends by the meter: if it sends or not the synchronous signal in the zone. |
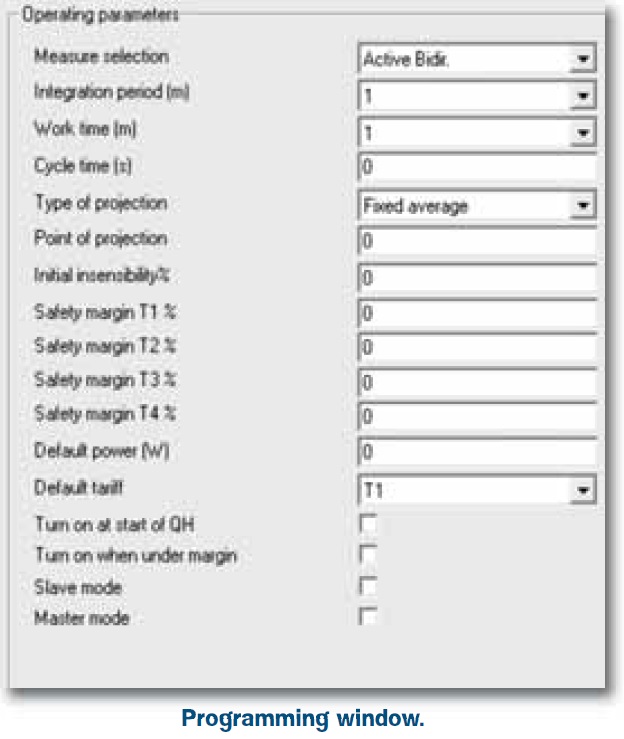
There are other configurable detailed parameters as:
|
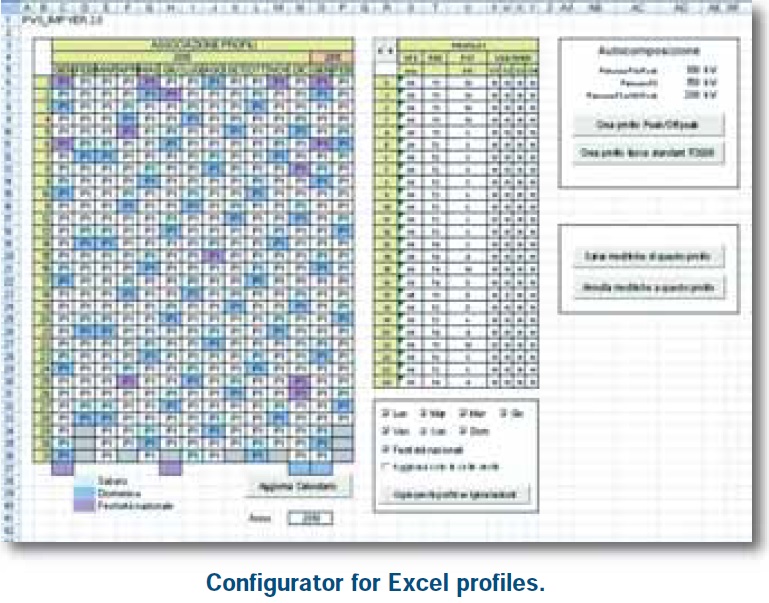
This detailed parameterization allows the best configuration of every situation and can satisfy all requirements. A specific application in Excel allows to prepare, save and send particular profiles of the equipment.
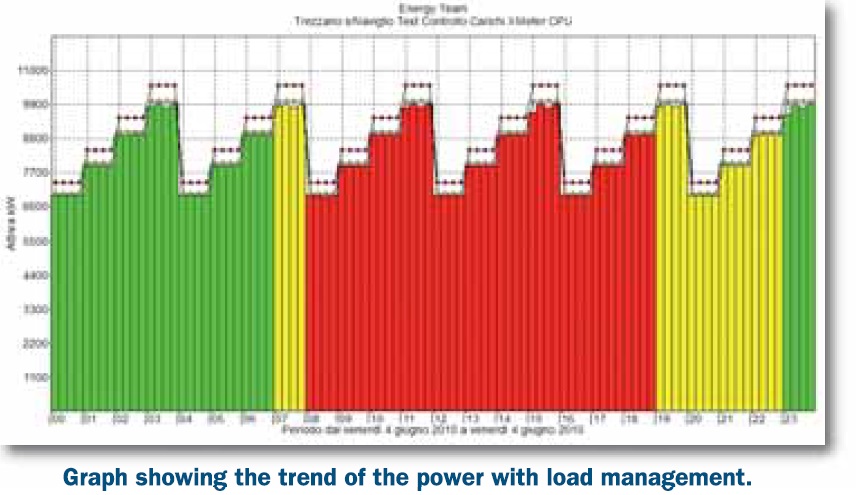
Load management is carried out using the “method of forecasting”. The interruption is driven when the expectation about total of consumption in the integration time, obtained by projecting the actual absorption-curve to the end of the time, goes over the set limit. The particular algorithm allows you to use at maximum the available energy within integration time, penalizing at the minimum the enabled loads which may be cut off. The load interruption is carried out as late as possible, considering also the quantity of energy that may be recovered by cutting it off, based also on the “weight” of the load. The advantage of this methodology is to avoid troublesome releases and reboots of the load in short times, which might occur if the hysteresis of each load isn’t considered. In order to avoid dangerous peaks in energy absorption, due to simultaneous restart of more loads, the systems foresees a method for inserting gradually the loads. The systems also allows you to check the loads which ask particular conditions of the plant for being released of restarted. For these loads, the action of the device may be inhibited if digital inputs don’t allow it (it’s essential for managing the consumers whose working depends by determined working phases). |
 |
Load management |





